Dicom MRI
Visualize a DICOM MRI scan. This demonstrates the flexible tensor slicing capabilities of the Rerun viewer.
Used Rerun types used-rerun-types
Background background
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) serves as a technical standard for the digital storage and transmission of medical images. In this instance, an MRI scan is visualized using Rerun.
Logging and visualizing with Rerun logging-and-visualizing-with-rerun
The visualizations in this example were created with just the following line.
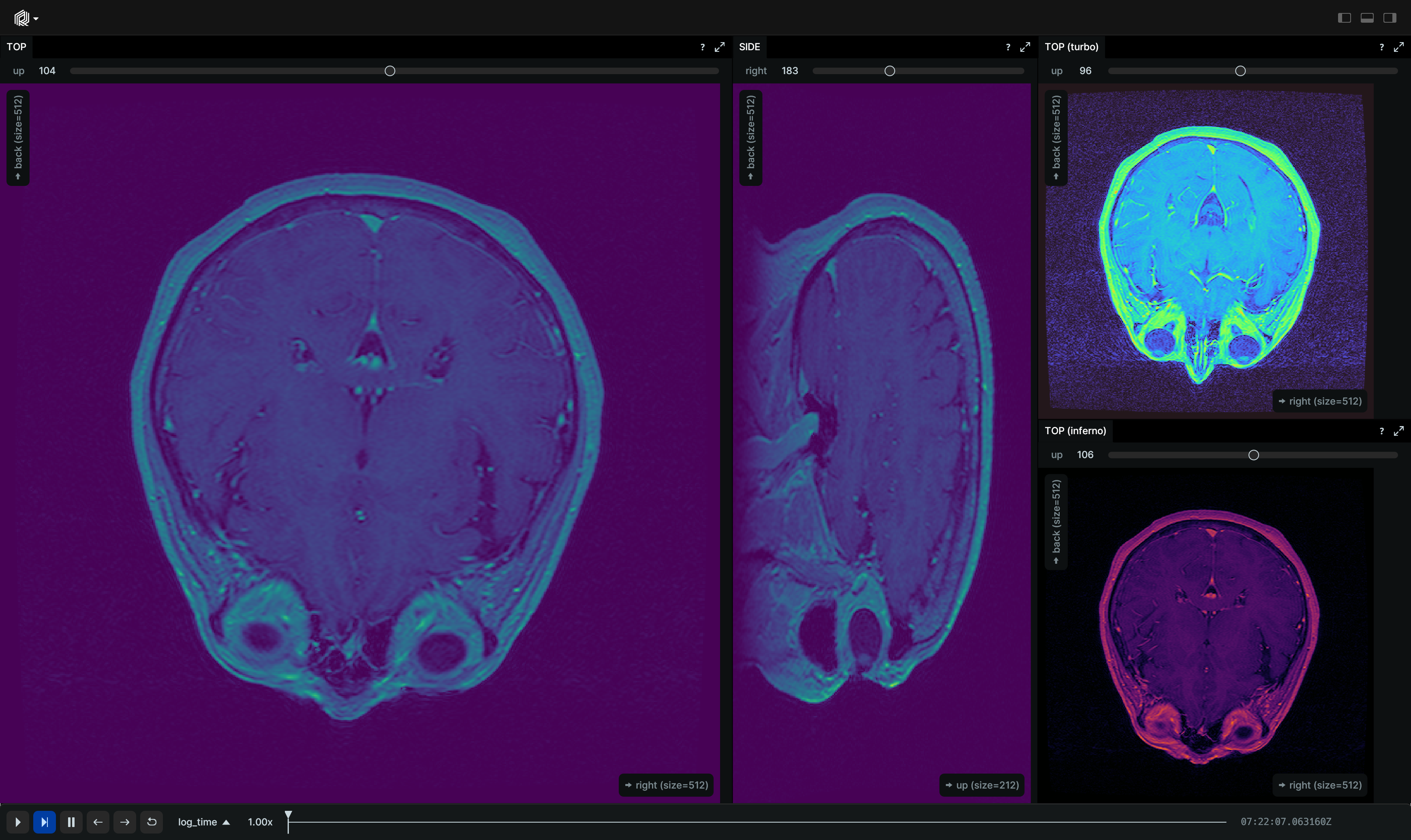
rr.log("tensor", rr.Tensor(voxels_volume_u16, dim_names=["right", "back", "up"]))A numpy.array named voxels_volume_u16 representing volumetric MRI intensities with a shape of (512, 512, 512).
To visualize this data effectively in Rerun, we can log the numpy.array as Tensor to the tensor entity.
In the Rerun Viewer you can also inspect the data in detail. The dim_names provided in the above call to rr.log help to
give semantic meaning to each axis. After selecting the tensor view, you can adjust various settings in the Blueprint
settings on the right-hand side. For example, you can adjust the color map, the brightness, which dimensions to show as
an image and which to select from, and more.
Run the code run-the-code
To run this example, make sure you have the Rerun repository checked out and the latest SDK installed:
pip install --upgrade rerun-sdk # install the latest Rerun SDK
git clone git@github.com:rerun-io/rerun.git # Clone the repository
cd rerun
git checkout latest # Check out the commit matching the latest SDK releaseInstall the necessary libraries specified in the requirements file:
pip install -e examples/python/dicom_mriTo experiment with the provided example, simply execute the main Python script:
python -m dicom_mri # run the exampleIf you wish to customize it, explore additional features, or save it, use the CLI with the --help option for guidance:
python -m dicom_mri --help